Difference between revisions of "Cheat sheet"
m (→Transitional (true) Δv) |
m (→Maps: *showing the image;) |
||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
==== Maps ==== | ==== Maps ==== | ||
| + | [[File:KerbinDeltaVMap.png|thumb|Δv to all bodies in the [[Kerbol System]]]] | ||
Various fan-made maps showing the Δv required to travel to a certain body. | Various fan-made maps showing the Δv required to travel to a certain body. | ||
'''Total Δv values''' | '''Total Δv values''' | ||
| − | |||
* http://www.skyrender.net/lp/ksp/system_map.png | * http://www.skyrender.net/lp/ksp/system_map.png | ||
'''Δv change values''' | '''Δv change values''' | ||
Revision as of 00:07, 3 July 2013
Kerbal Space Program rocket scientist's cheat sheet: Delta-v maps, equations and more for your reference so you can get from here to there and back again.
Contents
Mathematics
Delta-v (Δv)
Basic calculation
- → See also: Tutorial:Advanced Rocket Design
Basic calculation of a rocket's Δv. Use the atmospheric and vacuum thrust values for atmospheric and vacuum Δv, respectively.
Transitional (true) Δv
| Body | Δvout |
|---|---|
| Kerbin | 1000 m/s2 |
| other bodies' | data missing |
Calculation of a rocket's Δv, taking an atmosphere into account. Δvout is the amount of Δv required to leave a body's atmosphere, not reach orbit. This equation is useful to figure out the actual Δv of a stage that transitions from atmosphere to vacuum.
Maps
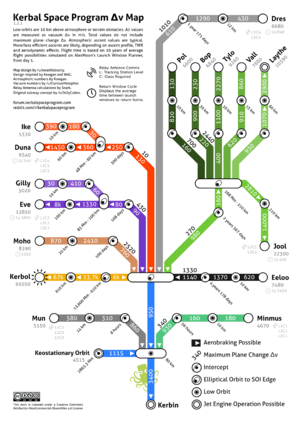
Various fan-made maps showing the Δv required to travel to a certain body.
Total Δv values
Δv change values
Δv nomogram
Thrust to weight ratio (TWR)
- → See also: Terminology
This is Newton's Second Law. If the ratio is less than 1 the craft will not lift off the ground.
Combined specific impulse (Isp)
If the Isp is the same for all engines in a stage, then the Isp is equal to a single engine. If the Isp is different for engines in a single stage, then use the following equation:
See also
Links to collections of reference material.



