Difference between revisions of "Maneuver node/zh-cn"
m |
|||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
| [[File:Retrograde.svg|32px|逆向]] | | [[File:Retrograde.svg|32px|逆向]] | ||
|} | |} | ||
| − | 这两个向量直接改变飞船的速度。向顺向点火会提高速度,并提升轨道对面的高度。而向逆向点火则会降低速度,并使轨道对面的高度降低。这两个符号都直接可以在[[navball|导航球]]中看到。 | + | 这两个向量直接改变飞船的速度。向顺向点火会提高速度,并提升轨道对面的高度。而向逆向点火则会降低速度,并使轨道对面的高度降低。这两个符号都直接可以在[[navball/zh-cn|导航球]]中看到。 |
这是改变轨道形状的最有效方法,所以只要可以,尽可能的使用这两个向量。 | 这是改变轨道形状的最有效方法,所以只要可以,尽可能的使用这两个向量。 | ||
| Line 44: | Line 44: | ||
选中一个节点后,会有六个符号出现。每个符号对应上述的六个向量之一。每个符号可以按住并拖动,拖动的方向会决定朝哪个方向改变dV,把一个符号朝变轨节点中心推和把与其对应的反向符号往外拉是等效的。另外,拖动的距离会影响调节的速率。 | 选中一个节点后,会有六个符号出现。每个符号对应上述的六个向量之一。每个符号可以按住并拖动,拖动的方向会决定朝哪个方向改变dV,把一个符号朝变轨节点中心推和把与其对应的反向符号往外拉是等效的。另外,拖动的距离会影响调节的速率。 | ||
| − | 添加变轨节点之后,三个新的数值会显示在[[navball|导航球]]上: | + | 添加变轨节点之后,三个新的数值会显示在[[navball/zh-cn|导航球]]上: |
# 所需的速度变化量,单位m/s | # 所需的速度变化量,单位m/s | ||
# 预测的加速所需耗时 | # 预测的加速所需耗时 | ||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
因为变轨表示的是一个瞬间的速度变化,所以实际上是无法完美地做到的。想要获得足够好的变轨节点,你需要提前大约一半加速所需耗时的时间来提前点火,而在经过该节点后的剩下一半时间完成剩余的加速。 | 因为变轨表示的是一个瞬间的速度变化,所以实际上是无法完美地做到的。想要获得足够好的变轨节点,你需要提前大约一半加速所需耗时的时间来提前点火,而在经过该节点后的剩下一半时间完成剩余的加速。 | ||
| − | 变轨节点可以用来达到一个特定的轨道,而不需要一直关注地图视角。在执行一个[[aerobraking|大气刹车]]机动时,当前的变轨节点会随着飞船速度减速而不断更新。这可以用来在大气刹车不足/过度时进行手动修正。 | + | 变轨节点可以用来达到一个特定的轨道,而不需要一直关注地图视角。在执行一个[[aerobraking/zh-cn|大气刹车]]机动时,当前的变轨节点会随着飞船速度减速而不断更新。这可以用来在大气刹车不足/过度时进行手动修正。 |
=== Prograde === | === Prograde === | ||
Revision as of 03:46, 23 October 2013
变轨节点表示轨道某个位置上的一次速度变化。你可以顺序添加多个变轨节点,且前面的变轨节点将会影响后面的。 添加节点后,它会显示你本次变轨所需的dV。如果有多个节点存在,只有第一个的所需dV会显示在导航球右上方,只有该变轨节点被删除后,下一个节点的dV信息才会显示在导航球右上方。
Contents
添加一个变轨节点
在地图视角中,单击飞船的轨道线,会弹出一个选项Add Maneuver让你添加变轨节点。节点创建后,选择节点并右键点击后会出现删除按钮。如果该变轨节点已经过时,选择该节点后会自动显示删除按钮。
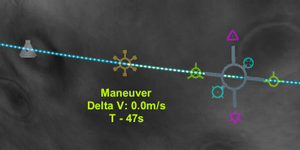
鼠标悬浮在一个节点上可以显示到达该节点的剩余时间以及这次变轨所需的Delta-V。
方向
因为运动在空间中(或空中)有三个维度,所以有三个轴可以加速,每个轴有两个方向。所有变轨操作都可以由这三个轴上的变化组合起来表示。
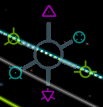
顺向及逆向
| |
|
这两个向量直接改变飞船的速度。向顺向点火会提高速度,并提升轨道对面的高度。而向逆向点火则会降低速度,并使轨道对面的高度降低。这两个符号都直接可以在导航球中看到。
这是改变轨道形状的最有效方法,所以只要可以,尽可能的使用这两个向量。
轨道平面法线/反面法线
| |
|
轨道平面法线/反面法线与轨道平面正交。对准这两个方向设置加速将会改变轨道倾角。在导航球上,这两个向量位于赤道线上,并且恰好处于 顺向 与 逆向 向量的中间。
这两个向量主要用于与另外一个星体/飞船进行轨道倾角对齐。而执行这个操作的最佳时机则是当飞船位于两者轨道平面的交线处。要与目标轨道倾角对齐,可以在升交点对准轨道平面反面法线设置加速,或在降交点对准轨道平面法线设置加速。 - 在设置加速的过程中,相对于该节点的倾角会接近0度,在极为接近0度时升/降交点会快速在轨道上移动,此时即说明加速量已经足够。
径向朝内/朝外
| |
|
径向朝内/外向量直接改变轨道是朝向星球还是远离星球(对应导航球上棕色/蓝色半球的中心点)。执行这样的变轨将会把轨道绕飞船旋转。这种变轨是最低效的变轨方式,顺向/逆向变轨要有效率的多。(译者注:但有时候这种方法非常有效,比如定点圆化轨道时)
在你从发射场垂直起飞时,你的飞船实际上就在执行远离星球的加速。
应用
选中一个节点后,会有六个符号出现。每个符号对应上述的六个向量之一。每个符号可以按住并拖动,拖动的方向会决定朝哪个方向改变dV,把一个符号朝变轨节点中心推和把与其对应的反向符号往外拉是等效的。另外,拖动的距离会影响调节的速率。
添加变轨节点之后,三个新的数值会显示在导航球上:
- 所需的速度变化量,单位m/s
- 预测的加速所需耗时
- 到达该节点的剩余时间(或者已经晚了多少时间)
因为变轨表示的是一个瞬间的速度变化,所以实际上是无法完美地做到的。想要获得足够好的变轨节点,你需要提前大约一半加速所需耗时的时间来提前点火,而在经过该节点后的剩下一半时间完成剩余的加速。
变轨节点可以用来达到一个特定的轨道,而不需要一直关注地图视角。在执行一个大气刹车机动时,当前的变轨节点会随着飞船速度减速而不断更新。这可以用来在大气刹车不足/过度时进行手动修正。
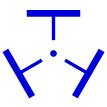
Prograde
This is the direction of your velocity (velocity=speed+direction) and is symbolized by a yellow circle with three little wings at 90 degree angles from each other, exactly the same as it appears on the navball.
Burning in this direction will increase your apoapsis or periapsis, depending on where you are in your orbit. Think of it as increasing what your height above the ground will be on the opposite side of your orbit. This has other applications but this should help you get the gist of it.
Retrograde
This is the opposite direction of your velocity and is symbolized by a yellow circle with a cross in it as well as three wings at a 120 degree angle from each other, exactly the same as it appears on the navball.
Burning in this direction will decrease your apoapsis or periapsis, depending on where you are in your orbit. Think of it as decreasing what your height above the ground will be on the opposite side of your orbit.
Normal
This direction is both perpendicular (i.e. forming a 90 degree angle) to the orbital plane (the plane formed by one complete orbit along a particular orbital path or line) and perpendicular to the orbited body's radial direction or parallel to the surface (i.e. in the same direction as). It is symbolized by a pink triangle with a dot in the center.
This direction has two major uses. Primarily, this maneuver is used to change the orbital plane by rotating it in the counter clock-wise direction (viewed from the side) around the point at which the burn takes place. The secondary use is to rendezvous with an orbiting object (ship, moon or planet); this is done by burning in this direction at the ascending node (i.e. the point at which your orbit intersects with the orbital plane of your target and begins passing beneath it)
Anti-normal
This direction is both perpendicular to the orbital plane and perpendicular to the orbited body's radial direction or parallel to the surface. It is also 180 degrees from Orbit Normal or in the opposite direction. It is symbolized by a pink triangle with little wings on each side.
This direction has two major uses. Primarily, this is used to make changes to the orbital plane by rotating in the clock-wise direction around the point at which the burn takes place. The secondary use is to rendezvous with an orbiting object (ship, moon, or planet); this is done by burring in this direction at the descending node (i.e. the point at which your orbit intersects with the orbital plane of your target and begins passing above it).
Radial in
This direction points in the direction of the orbited body, i.e. it is perpendicular to the surface of the orbited body. It is also perpendicular to the direction of travel and Orbit Normal. It is symbolized by a blue circle with what looks like a four leaf clover in it (actually 4 inward wings).
This direction is used to rotate the orbit about the point of burn without changing the orbital plane (think spinning a hula hoop with a stick). This direction will rotate the orbit counter-clockwise with a maximum change in angle of less than 90 degrees; beyond this point, the orbit would pass through the center of mass of the orbited body, and the ship would traverse a slow spiral in towards the center of mass of the orbited body.
This is primarily used in rendezvous to line up two irregular orbits.
Radial out
This direction points away from of the orbited body; also, it is perpendicular to the surface of the orbited body. It is also perpendicular to the direction of travel and Orbit Normal. It is symbolized by a blue circle with a dot in the center and four wings at 90 degrees from each other.
This direction is used to rotate the orbit about the point of burn without changing the orbital plane. This direction will rotate the orbit clockwise with a maximum change in angle of less than 90 degrees; beyond this point, all horizontal momentum would be cancelled (this not possible in real life, but it is possible in Kerbal Space Program; normally, the ship would traverse a slow spiral away from the center of mass of the orbited body).
This is primarily used in rendezvous to line up two irregular orbits.
点火加速
想要达成预定的变轨,你需要在适当的时机开始点火。对于时间较长的变轨,你需要提前大约一半的时间开始加速,并在到达节点后再花一半时间完成加速。
如果飞船装备了SAS,你可以在设置好变轨节点后就将飞船对准蓝色符号(见截图) - 一旦变轨设计完,加速的方向就已经确定,无论飞船处于什么地方。
当你即将要完成加速时,蓝色符号会开始从你的当前方向移开,这主要是因为你的方向无法完全对准蓝色符号,一般来说,因为误差足够小,这一点可以忽略。(译者注:你也可以用RCS平移来做最后的精确修正)
当你完成变轨后(导航球右方的dV下降到0或极小的一个数字时),将油门收起(按X键)以避免加速过头。此时蓝色符号朝向哪里已经没有什么意义了,你可以到地图视角删除该节点。当你有多个变轨节点时这一点尤为重要,因为在你删除当前节点之前,下一个节点的信息不会显示出来。