Difference between revisions of "Tutorial: Advanced Orbiting"
m (→Finally) |
(→Planets outside your original orbit) |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
If you are meeting with a planet whose orbit is outside of your starting orbit, create a transfer orbit such that your apoapsis is as close as possible to your target planet's orbit. | If you are meeting with a planet whose orbit is outside of your starting orbit, create a transfer orbit such that your apoapsis is as close as possible to your target planet's orbit. | ||
| − | + | To meet the target planet, you will have to rotate the apoapsis of your transfer orbit until it reaches a point where your ship will arrive at the same time as the planet (this is better (more sophisticated and interesting) than simply orbiting until they randomly come in contact). The orbit map has a couple features to aid you in this. In the orbit map, right click on the object with which you want to rendevous, and set it as the target. Then you will see some new information on the map. First it will mark where on the orbit the ascending and descending nodes of the target orbit are--see above for changing inclination. Second, you will see one or two markers for "intersect points." The first is the point where the orbits are closest, the second is where the target body will be when the orbits intersect. | |
==== Planets inside your original orbit ==== | ==== Planets inside your original orbit ==== | ||
Revision as of 14:19, 19 January 2015
Contents
Hohmann transfer
Burn prograde at periapsis (or anywhere if circular) until the apoapsis reaches the desired altitude.
Then, at apoapsis, burn prograde until periapsis is at the desired altitude.
Burning retrograde at these same points will lower your orbit.
Bi-elliptical transfer
The bi-elliptic transfer can be more efficient (but slower) than the Hohmann transfer orbit in some cases (when going from a very tight orbit to a very large one: the ratio must be higher than ~12:1). This is because changes of speed are more efficient at low speeds (and therefore at high altitudes).
- Start by burning prograde until your orbit becomes highly elliptical (the apoapsis must then be higher than both orbits).
- At apoapsis, burn prograde until the periapsis reaches the altitude of your desired orbit.
- Once reaching periapsis, burn retrograde until your orbit is circularized.
Opposite burns at these same points will lower your orbit. This can be used to allow you to use aerobraking to lower your orbit height.
Orbital plane alignment
The first step in intercepting another orbiting body is to align your orbital plane with the target's orbital plane.
Next is to find the pivot point on your orbit that, when turned clockwise or counterclockwise (from the perspective of camera > ship > orbited object), will cause it to line up with the other orbit.
Next, find the midpoint between your prograde and retrograde motion on the horizon and point your ship toward it. Throttling prograde + 90 degrees on the horizon will cause your orbit to rotate clockwise. Prograde - 90 degrees on the horizon will rotate the orbit counterclockwise. It may take a few rotation sessions to perfect your orbit but this will allow you to match another orbital plane.
It is easier to achieve if your orbit is circular, mostly because you can line up the orbits in the map view much more easily.
Orbit synchronization
In progress.
The Exley maneuver
(As of 0.17.1)
In order to easily meet with a target planet's sphere of influence, you will need to perform a few burns while at either the periapsis or apoapsis of your transfer orbit.
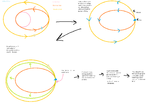
Planets outside your original orbit
If you are meeting with a planet whose orbit is outside of your starting orbit, create a transfer orbit such that your apoapsis is as close as possible to your target planet's orbit.
To meet the target planet, you will have to rotate the apoapsis of your transfer orbit until it reaches a point where your ship will arrive at the same time as the planet (this is better (more sophisticated and interesting) than simply orbiting until they randomly come in contact). The orbit map has a couple features to aid you in this. In the orbit map, right click on the object with which you want to rendevous, and set it as the target. Then you will see some new information on the map. First it will mark where on the orbit the ascending and descending nodes of the target orbit are--see above for changing inclination. Second, you will see one or two markers for "intersect points." The first is the point where the orbits are closest, the second is where the target body will be when the orbits intersect.
Planets inside your original orbit
If you are meeting with a planet whose orbit is inside of your starting orbit, create a transfer orbit such that your periapsis is as close as possible to your target planet's orbit.
Next, make a few orbits until the target planet is slightly behind you when you reach your periapsis. Begin a retrograde burn until you see your orbit cross the target planet's near your periapsis for a fraction of a second. If you overshoot, simply turn around and burn prograde until the cross orbit is visible again. If your transfer orbit goes within the planet's orbit, then you have gone too far, and have either missed the cross orbit, or do not have a periapsis close enough to the target orbit to be affected by the planet's sphere of influence.
Finally
Once you are in the cross orbit, burn retrograde until the orbit goes around your target planet.
Good luck!