Difference between revisions of "Orbit"
(+some properties;) |
(rv - Various reasons; see talk) |
||
| (32 intermediate revisions by 17 users not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
== Properties == | == Properties == | ||
| − | Each orbit has some basic properties which | + | Each orbit has some basic properties which characterize them. This list contains multiple values which can be calculated using other properties of the list. |
=== Apoapsis and periapsis === | === Apoapsis and periapsis === | ||
{{See also||{{Wikipedia|Apsis}}}} | {{See also||{{Wikipedia|Apsis}}}} | ||
| − | The apsides | + | The apsides are the nearest and farthest points of the orbit. The periapsis is the lowest point of the orbit and is helpful to determine if the orbit is high enough to avoid collisions with the surface or interaction with an atmosphere. The apoapsis is on the other side of the orbit and the furthest point away from the orbited celestial body. The periapsis is not shown if it lies under the surface. There might be confusion about from which point the apsides are measured. In game they are shown from the surface, while for orbital mechanics usually the values from the center of the body are relevant. A craft after the most recent apoapsis and before the periapsis is falling towards the surface while a craft after the most recent periapsis and before the apoapsis is rising. |
| − | + | For parabolic and hyperbolic trajectories, there is no apoapsis as it the curve it describes is open. Apoapsides in other spheres of influence are possible. The periapsis of such a trajectory is only shown if it is in the future, and as soon as the craft passes through the periapsis and is rising it vanishes. Like apoapsides, periapsides in other spheres of influence are possible. | |
| + | |||
| + | In perfect circular orbits it is not possible to determine the apsides. The altitude, which is always the same for the orbit, is used for the apsides if required. They are identical to the semi-major axis when measured from the center. Elliptical orbits have usually both apsides and only no periapsis if it is below the surface. If an orbit is almost circular it is usually treated as perfectly circular where both apsides and the semi-major axis are identical if measured from the body's center. | ||
Sometimes there are special words used for the different bodies. Apokee or apokerb for the apoapsis of an orbit around [[Kerbin]] and similar perikee or perikerb for the periapsis around Kerbin. | Sometimes there are special words used for the different bodies. Apokee or apokerb for the apoapsis of an orbit around [[Kerbin]] and similar perikee or perikerb for the periapsis around Kerbin. | ||
| + | |||
| + | In Kerbal Space Program the apsides are usually abbreviated to “Ap” and “Pe” which corresponds with the two markers on the orbit. In real world science an uppercase <tt>Q</tt> is used for apoapsides and a lowercase <tt>q</tt> for periapsides because variables usually only contain one letter. Using <tt>a</tt> for the apoapsis is not recommended as it can generate confusion with the semi-major axis which usually uses that variable name. | ||
=== Eccentricity === | === Eccentricity === | ||
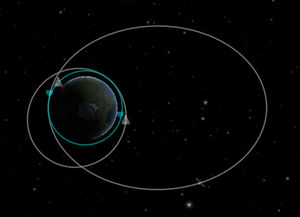
[[File:KerbalEccentricity.jpg|thumb|Eccentric orbits (white) and a non-eccentric orbit (blue)]] | [[File:KerbalEccentricity.jpg|thumb|Eccentric orbits (white) and a non-eccentric orbit (blue)]] | ||
{{See also||{{Wikipedia|Orbital eccentricity}}}} | {{See also||{{Wikipedia|Orbital eccentricity}}}} | ||
| − | The eccentricity gives how | + | The eccentricity gives how circular the orbit is. There are different eccentricities, although usually the orbital eccentricity is used for orbital mechanics. It can categorised in four categories: |
* In a circular orbit the eccentricity is exactly 0 | * In a circular orbit the eccentricity is exactly 0 | ||
* In an elliptical orbit the eccentricity is between 0 and 1 | * In an elliptical orbit the eccentricity is between 0 and 1 | ||
* In a parabolic orbit the eccentricity is exactly 1 | * In a parabolic orbit the eccentricity is exactly 1 | ||
* In a hyperbolic orbit the eccentricity is above 1 | * In a hyperbolic orbit the eccentricity is above 1 | ||
| − | If the eccentricity is above or equal to 1 the orbit is escaping the body. Circular and parabolic orbits are not common if not impossible, as the maneuvers have to be extremely precise. | + | If the eccentricity is above or equal to 1 the orbit is escaping the body. Circular and parabolic orbits are not common if not impossible, as the maneuvers have to be extremely precise. It is possible, however, to get the eccentricity very close to 0 or 1 which can then be considered as circular or parabolic respectively. Some planets and moons in Kerbal Space Program have a perfectly circular orbit because they move on “rails”; no physical interaction can change the properties. |
| + | |||
| + | However, an orbit with an eccentricity below 1 can also escape the [[sphere of influence]] because the eccentricity is based on the ratio of the apsides; It doesn't take account of the remaining distance between the apoapsis and the body's SOI. A circular orbit close to the edge of the sphere of influence has an eccentricity of 0, but as soon as the apoapsis is marginally increased the orbit leaves the sphere of influence, disregarding the fact that the eccentricity is still close to zero. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The eccentricity is usually abbreviated by a lowercase <tt>e</tt>. It can be calculated in-game by (Ap - Pe)/(2R + Ap + Pe), where Ap is the apoapsis, Pe is the periapsis, and R is the radius of the parent body. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Orbital speed === | ||
| + | {{Main article||{{Wikipedia|Orbital speed}}}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | The orbital speed of a celestial body, craft or object is the speed of the object relative to the barycenter (center of mass) of the two-body system. The game considers the barycenter to always coincide with the center of the orbited body. Orbital speed is dependent upon the mass of the orbited body and the semi-major axis of the orbit. For circular orbits, orbital speed is constant throughout the orbit, while elliptical or hyperbolic orbits will have a maximum speed at periapsis and minimum speed at apoapsis or sphere of influence entry/exit respectively. | ||
| + | |||
| + | {{See also|List of orbital velocities for low orbit}} | ||
=== Inclination === | === Inclination === | ||
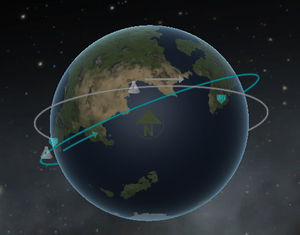
[[File:Kerbalinclinedorbit.jpg|thumb|The blue orbit has an inclination of 20° while the grey has none.]] | [[File:Kerbalinclinedorbit.jpg|thumb|The blue orbit has an inclination of 20° while the grey has none.]] | ||
| − | {{ | + | {{Main article||{{Wikipedia|Orbital inclination}}}} |
The tilt of the orbit is given by the inclination. Usually the value is given in degrees where the value is given between –90° and 270°. An inclination of 0° or 180° is equatorial, so the craft is always above the equator. An inclination of 90° is characteristic for polar orbits. When the inclination is below 90° the orbit is prograde, meaning the rotation around the body is the same as the rotation of the body. An inclination above 90° and below 270° determines a retrograde orbit which orbits the other way around. As all bodies in the [[Kerbol System]] are rotate counter-clockwise, seen from the North pole, all prograde orbits are counter-clockwise and all retrograde orbits are clockwise. | The tilt of the orbit is given by the inclination. Usually the value is given in degrees where the value is given between –90° and 270°. An inclination of 0° or 180° is equatorial, so the craft is always above the equator. An inclination of 90° is characteristic for polar orbits. When the inclination is below 90° the orbit is prograde, meaning the rotation around the body is the same as the rotation of the body. An inclination above 90° and below 270° determines a retrograde orbit which orbits the other way around. As all bodies in the [[Kerbol System]] are rotate counter-clockwise, seen from the North pole, all prograde orbits are counter-clockwise and all retrograde orbits are clockwise. | ||
| − | Depending from the starting location the directly available lowest inclination is limited to the latitude. A polar orbit is always possible, while for equatorial orbits the craft has to start from the equator. As the [[Kerbal Space Center]] is near the equator it is possible to launch into almost all inclinations without additional orbital | + | Depending from the starting location the directly available lowest inclination is limited to the latitude. A polar orbit is always possible, while for equatorial orbits the craft has to start from the equator. As the [[Kerbal Space Center]] is near the equator it is possible to launch into almost all inclinations without additional orbital maneuvers. |
| − | While a polar orbit, and depending on the altitude and coverage also near polar inclinations, covers a complete body, rendezvous with an object in | + | While a polar orbit, and depending on the altitude and coverage also near polar inclinations, covers a complete body, rendezvous with an object in an equatorial orbit is usually easier. The inclination is exactly the range of latitudes the craft will pass over in both (North and South) direction. |
| − | + | Current orbital inclination is visible on the "Advanced Orbital Info" tab in "Maneuver Mode" on the bottom left panel. | |
| + | |||
| + | The inclination is given in most cases relative to the parent's equator, but especially the inclination of the [[planet]]s can be given relative to the ecliptic. The ecliptic is the orbital plane of Kerbin because the inclination relative to Kerbol's equator is 0°, meaning that there is no difference between the inclination relative to Kerbol's equator and the ecliptic. | ||
=== Semi-major axis === | === Semi-major axis === | ||
{{See also||{{Wikipedia|Semi-major axis}}}} | {{See also||{{Wikipedia|Semi-major axis}}}} | ||
| + | <!-- commenting out as currently broken <math class="float-left">a = \frac{Q+q}{2}</math> -- I used the one letter versions as (la)tex treats multiletter variables as multiplication. E.g. sma is shown with little whitespaces which might be interpreted as s·m·a --> | ||
The semi-major axis is the average of the apsides and usually measured from the body's center. The semi-major axis cannot be directly measured in game without mods, but it is easy to calculate by dividing the sums of the apsides by two. The semi-major axis defines the orbital period, so no matter how elongated the orbit is, as long as the semi-major axis stays the same, the orbital period doesn't change. This makes [[synchronous orbit]]s easier to achieve, as the circularity is only important for stationary orbits. | The semi-major axis is the average of the apsides and usually measured from the body's center. The semi-major axis cannot be directly measured in game without mods, but it is easy to calculate by dividing the sums of the apsides by two. The semi-major axis defines the orbital period, so no matter how elongated the orbit is, as long as the semi-major axis stays the same, the orbital period doesn't change. This makes [[synchronous orbit]]s easier to achieve, as the circularity is only important for stationary orbits. | ||
| + | |||
| + | If the apsides are given from the body's surface the same formula can be used but the resulting value has to be added by the radius of the body. The semi-major axis may be used as the average distance, but it depends on the definition of which average distance is meant. In formula the semi-major axis is usually abbreviated by a lowercase <tt>a</tt> which shouldn't be confused with the apoapsis. | ||
== Types of orbits == | == Types of orbits == | ||
| + | <span id="LKO"></span> | ||
=== Low Kerbin orbit (LKO) === | === Low Kerbin orbit (LKO) === | ||
| − | In analogy to the real world ''low Earth orbit (LEO)'' | + | In analogy to the real world ''low Earth orbit (LEO)'' a LKO describes a stable low orbit around [[Kerbin]] that can be achieved with relatively low cost of [[Delta-V]]. The lowest point of an LKO must not be lower than 70 km in order to stay clear of [[atmosphere|atmospheric]] drag. The altitude of a LKO typically does not exceed about 200 km. |
Tons of [[payload]] delivered to LKO is often used to compare performance and size of launch vehicles. | Tons of [[payload]] delivered to LKO is often used to compare performance and size of launch vehicles. | ||
| − | In optimal circumstances LKO can be achieved with | + | In optimal circumstances LKO can be achieved with 3,200-3,400 m/s Delta-V.<ref>[https://i.imgur.com/yO0bQax.png Kerbin delta-V chart]</ref> |
Due to the [[w:Oberth effect|Oberth effect]] a low orbit is a suitable starting point for transferring to other celestial bodies. {{cn}} | Due to the [[w:Oberth effect|Oberth effect]] a low orbit is a suitable starting point for transferring to other celestial bodies. {{cn}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <span id="HKO"></span> | ||
| + | === High Kerbin orbit (HKO) === | ||
| + | In analogy to the real world ''high Earth orbit (HEO)'' a HKO describes a stable high orbit around [[Kerbin]]. The altitude of a HKO typically is higher than the KEO (2863.33 km). | ||
=== Stationary orbit and synchronous orbit === | === Stationary orbit and synchronous orbit === | ||
| − | {{Main article| | + | {{Main article|Synchronous orbit}} |
An orbit with the same orbital period as the rotational period of the orbited body is called a synchronous orbit. If the inclination is also 0° and there is no eccentricity it is called a stationary orbit. A satellite in this orbit doesn't appear to move when viewed from the body's surface. | An orbit with the same orbital period as the rotational period of the orbited body is called a synchronous orbit. If the inclination is also 0° and there is no eccentricity it is called a stationary orbit. A satellite in this orbit doesn't appear to move when viewed from the body's surface. | ||
| − | === Kerbisynchronous | + | <span id="KEO"></span> |
| + | === Kerbisynchronous equatorial orbit (KEO) === | ||
{{Main article|KEO}} | {{Main article|KEO}} | ||
The stationary orbit around Kerbin, where the orbiting craft appears to stand still at a point above Kerbin's equator. The name was chosen to abbreviate it similar to ''GEO'' the abbreviation for ''geostationary orbit'', which is the real world equivalent on the Earth. | The stationary orbit around Kerbin, where the orbiting craft appears to stand still at a point above Kerbin's equator. The name was chosen to abbreviate it similar to ''GEO'' the abbreviation for ''geostationary orbit'', which is the real world equivalent on the Earth. | ||
| Line 63: | Line 89: | ||
=== Other === | === Other === | ||
Various other orbits can be defined. The [[w:List of orbits|list of orbits]] on Wikipedia contain many common ones in the real world. They can be recreated by modifying the core features of the orbit to match the smaller universe. Some kind of orbits, like a sun-synchronous orbit around Earth, are not possible, because they require Kerbin's gravity to be not perfect. Also the Lagrange points do not exist so orbits near/around a Lagrange point are impossible. But it is possible to imitate L<sub>4</sub> and L<sub>5</sub>, although every orbit with the same semi-major axis has the same orbital period, so L<sub>4</sub> and L<sub>5</sub> aren't special positions then. | Various other orbits can be defined. The [[w:List of orbits|list of orbits]] on Wikipedia contain many common ones in the real world. They can be recreated by modifying the core features of the orbit to match the smaller universe. Some kind of orbits, like a sun-synchronous orbit around Earth, are not possible, because they require Kerbin's gravity to be not perfect. Also the Lagrange points do not exist so orbits near/around a Lagrange point are impossible. But it is possible to imitate L<sub>4</sub> and L<sub>5</sub>, although every orbit with the same semi-major axis has the same orbital period, so L<sub>4</sub> and L<sub>5</sub> aren't special positions then. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Suborbital === | ||
| + | An orbit is suborbital if the periapsis is below the surface and/or [[atmosphere]](if the orbited body has one). A craft on a suborbital trajectory will most likely crash into the surface or land on it without finishing a complete orbit. Lifting surfaces like [[wing]]s and parachutes might delay this. | ||
== Orbits in the save file == | == Orbits in the save file == | ||
| − | The save files (and scenarios) in KSP are plain text and human readable | + | The save files (and scenarios) in KSP are plain text and human readable with the information on the orbit of every craft currently in the game. Most text editors allow to search for <code>name = [Name of craft]</code> via {{Key press|Ctrl|F}} ({{Key press|⌘Cmnd|F}} for Mac). This locates the craft quickly in the file. The orbit section of the persistent.sfs should looks something like this: |
ORBIT | ORBIT | ||
| Line 80: | Line 109: | ||
} | } | ||
| − | Each of these terms has a meaning | + | Each of these terms has a physical meaning and together they define an orbit. Changing them (and then re-loading the save game) will change the orbit of the vessel in question. |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | The first five parameters uniquely define a Keplerian trajectory: | |
| − | * INC | + | * '''Eccentricity''' (ECC) and '''semimajor axis''' (SMA) specify, respectively, the shape of the trajectory (0 = circular, < 1 = elliptic, 1 = parabolic, > 1 = hyperbolic) and its size (half the distance between apsides, or equivalently, average of apsides as measured from the centre of the body). Hyperbolic orbits have a negative "semimajor axis" which relates to the mathematical definition of a hyperbola as a mirrored pair of curves, of which the orbit is one branch. However due to KSP's system of spheres of influence, an object can have an elliptic orbit (positive semimajor axis and eccentricity below 1) and still be escaping. |
| − | * | + | * '''Inclination''' (INC) and '''longitude of ascending node''' (LAN) specify the tilt of the orbital plane (anticlockwise from the ecliptic at the ascending node) and its orientation (anticlockwise from the vernal point to the ascending node). On Earth, the vernal point is the point on the celestial sphere where the sun is at the vernal equinox in the northern hemisphere (the ascending node of the ecliptic relative to the celestial equator). Since Kerbin has no axial tilt, the vernal point is arbitrary. |
| − | + | * '''Longitude of periapsis''' (LPE) specifies the orientation of the orbit within its plane (angle anticlockwise from the ascending node to the periapsis). | |
| − | + | Then the object's position on the orbit at a given time is extrapolated from | |
| − | * EPH | + | * '''Epoch''' (EPH), a reference time, and |
| − | * REF : reference | + | * '''Mean anomaly at epoch''' (MNA), a pseudo-angle (up to 2π) expressing the proportion of the orbital period that has passed since last periapsis. It's the angle of the corresponding position on a circular orbit. For hyperbolic orbits, this is negative if approaching periapsis, positive if receding from it. |
| − | * OBJ : Some sort of object reference (I wouldn't change this number). | + | These numbers are put into context by: |
| + | * REF : a reference number giving the celestial body that the object is orbiting. See below for a table. | ||
| + | * OBJ : Some sort of object reference (I wouldn't change this number). Possibly a code for the icon displayed - it appears that 0 corresponds to probes, and 1 corresponds to debris. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Angles are in radians, distances in meters. | ||
By altering these values in the save file, one can easily "slew" vehicles into any position desired. This is very useful for setting up scenarios. | By altering these values in the save file, one can easily "slew" vehicles into any position desired. This is very useful for setting up scenarios. | ||
| Line 159: | Line 192: | ||
* {{Wikipedia|Apsis}} | * {{Wikipedia|Apsis}} | ||
* {{Wikipedia|Low Earth orbit}} | * {{Wikipedia|Low Earth orbit}} | ||
| + | * Kraft, D and Townsend, G. (1963). ''NASA Orbital Flight Handbook, Part 1 - Basic Techniques and Data''. Space Flight Handbooks, Vol. 1. http://ntrs.nasa.gov/search.jsp?R=19630011221 | ||
| + | ** For an enormous table of Keplerian element equations, see pdf page 126/document page III-16. | ||
Latest revision as of 09:02, 3 January 2024
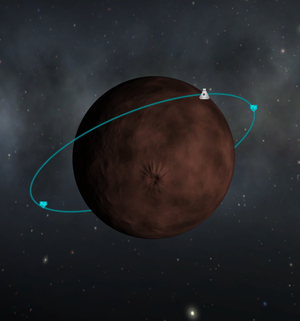
An orbit is an elliptical path around a celestial body. The point on an orbit which is closest to the orbited body is called the periapsis and the furthest point is the apoapsis. These points are indicated on the map view as "Pe" and "Ap", respectively.
An orbit is considered “stable” if all points in the orbit are above the terrain and atmosphere of the orbited body, which applies if the periapsis is above the terrain and atmosphere as this is the lowest point of the orbit. A spacecraft in such an orbit will not lose velocity due to atmospheric drag and won't collide with terrain.
To achieve an orbit, a spacecraft must reach a sufficient altitude and orbital velocity. During ascent, a gravity turn helps to achieve both of these goals in a fuel-efficient way. With basic maneuvers it is possible to change the orbital shape.
Properties
Each orbit has some basic properties which characterize them. This list contains multiple values which can be calculated using other properties of the list.
Apoapsis and periapsis
- → See also: Apsis on Wikipedia
The apsides are the nearest and farthest points of the orbit. The periapsis is the lowest point of the orbit and is helpful to determine if the orbit is high enough to avoid collisions with the surface or interaction with an atmosphere. The apoapsis is on the other side of the orbit and the furthest point away from the orbited celestial body. The periapsis is not shown if it lies under the surface. There might be confusion about from which point the apsides are measured. In game they are shown from the surface, while for orbital mechanics usually the values from the center of the body are relevant. A craft after the most recent apoapsis and before the periapsis is falling towards the surface while a craft after the most recent periapsis and before the apoapsis is rising.
For parabolic and hyperbolic trajectories, there is no apoapsis as it the curve it describes is open. Apoapsides in other spheres of influence are possible. The periapsis of such a trajectory is only shown if it is in the future, and as soon as the craft passes through the periapsis and is rising it vanishes. Like apoapsides, periapsides in other spheres of influence are possible.
In perfect circular orbits it is not possible to determine the apsides. The altitude, which is always the same for the orbit, is used for the apsides if required. They are identical to the semi-major axis when measured from the center. Elliptical orbits have usually both apsides and only no periapsis if it is below the surface. If an orbit is almost circular it is usually treated as perfectly circular where both apsides and the semi-major axis are identical if measured from the body's center.
Sometimes there are special words used for the different bodies. Apokee or apokerb for the apoapsis of an orbit around Kerbin and similar perikee or perikerb for the periapsis around Kerbin.
In Kerbal Space Program the apsides are usually abbreviated to “Ap” and “Pe” which corresponds with the two markers on the orbit. In real world science an uppercase Q is used for apoapsides and a lowercase q for periapsides because variables usually only contain one letter. Using a for the apoapsis is not recommended as it can generate confusion with the semi-major axis which usually uses that variable name.
Eccentricity
- → See also: Orbital eccentricity on Wikipedia
The eccentricity gives how circular the orbit is. There are different eccentricities, although usually the orbital eccentricity is used for orbital mechanics. It can categorised in four categories:
- In a circular orbit the eccentricity is exactly 0
- In an elliptical orbit the eccentricity is between 0 and 1
- In a parabolic orbit the eccentricity is exactly 1
- In a hyperbolic orbit the eccentricity is above 1
If the eccentricity is above or equal to 1 the orbit is escaping the body. Circular and parabolic orbits are not common if not impossible, as the maneuvers have to be extremely precise. It is possible, however, to get the eccentricity very close to 0 or 1 which can then be considered as circular or parabolic respectively. Some planets and moons in Kerbal Space Program have a perfectly circular orbit because they move on “rails”; no physical interaction can change the properties.
However, an orbit with an eccentricity below 1 can also escape the sphere of influence because the eccentricity is based on the ratio of the apsides; It doesn't take account of the remaining distance between the apoapsis and the body's SOI. A circular orbit close to the edge of the sphere of influence has an eccentricity of 0, but as soon as the apoapsis is marginally increased the orbit leaves the sphere of influence, disregarding the fact that the eccentricity is still close to zero.
The eccentricity is usually abbreviated by a lowercase e. It can be calculated in-game by (Ap - Pe)/(2R + Ap + Pe), where Ap is the apoapsis, Pe is the periapsis, and R is the radius of the parent body.
Orbital speed
- → Main article: Orbital speed on Wikipedia
The orbital speed of a celestial body, craft or object is the speed of the object relative to the barycenter (center of mass) of the two-body system. The game considers the barycenter to always coincide with the center of the orbited body. Orbital speed is dependent upon the mass of the orbited body and the semi-major axis of the orbit. For circular orbits, orbital speed is constant throughout the orbit, while elliptical or hyperbolic orbits will have a maximum speed at periapsis and minimum speed at apoapsis or sphere of influence entry/exit respectively.
- → See also: List of orbital velocities for low orbit
Inclination
- → Main article: Orbital inclination on Wikipedia
The tilt of the orbit is given by the inclination. Usually the value is given in degrees where the value is given between –90° and 270°. An inclination of 0° or 180° is equatorial, so the craft is always above the equator. An inclination of 90° is characteristic for polar orbits. When the inclination is below 90° the orbit is prograde, meaning the rotation around the body is the same as the rotation of the body. An inclination above 90° and below 270° determines a retrograde orbit which orbits the other way around. As all bodies in the Kerbol System are rotate counter-clockwise, seen from the North pole, all prograde orbits are counter-clockwise and all retrograde orbits are clockwise.
Depending from the starting location the directly available lowest inclination is limited to the latitude. A polar orbit is always possible, while for equatorial orbits the craft has to start from the equator. As the Kerbal Space Center is near the equator it is possible to launch into almost all inclinations without additional orbital maneuvers.
While a polar orbit, and depending on the altitude and coverage also near polar inclinations, covers a complete body, rendezvous with an object in an equatorial orbit is usually easier. The inclination is exactly the range of latitudes the craft will pass over in both (North and South) direction.
Current orbital inclination is visible on the "Advanced Orbital Info" tab in "Maneuver Mode" on the bottom left panel.
The inclination is given in most cases relative to the parent's equator, but especially the inclination of the planets can be given relative to the ecliptic. The ecliptic is the orbital plane of Kerbin because the inclination relative to Kerbol's equator is 0°, meaning that there is no difference between the inclination relative to Kerbol's equator and the ecliptic.
Semi-major axis
- → See also: Semi-major axis on Wikipedia
The semi-major axis is the average of the apsides and usually measured from the body's center. The semi-major axis cannot be directly measured in game without mods, but it is easy to calculate by dividing the sums of the apsides by two. The semi-major axis defines the orbital period, so no matter how elongated the orbit is, as long as the semi-major axis stays the same, the orbital period doesn't change. This makes synchronous orbits easier to achieve, as the circularity is only important for stationary orbits.
If the apsides are given from the body's surface the same formula can be used but the resulting value has to be added by the radius of the body. The semi-major axis may be used as the average distance, but it depends on the definition of which average distance is meant. In formula the semi-major axis is usually abbreviated by a lowercase a which shouldn't be confused with the apoapsis.
Types of orbits
Low Kerbin orbit (LKO)
In analogy to the real world low Earth orbit (LEO) a LKO describes a stable low orbit around Kerbin that can be achieved with relatively low cost of Delta-V. The lowest point of an LKO must not be lower than 70 km in order to stay clear of atmospheric drag. The altitude of a LKO typically does not exceed about 200 km.
Tons of payload delivered to LKO is often used to compare performance and size of launch vehicles.
In optimal circumstances LKO can be achieved with 3,200-3,400 m/s Delta-V.[1]
Due to the Oberth effect a low orbit is a suitable starting point for transferring to other celestial bodies. [citation needed]
High Kerbin orbit (HKO)
In analogy to the real world high Earth orbit (HEO) a HKO describes a stable high orbit around Kerbin. The altitude of a HKO typically is higher than the KEO (2863.33 km).
Stationary orbit and synchronous orbit
- → Main article: Synchronous orbit
An orbit with the same orbital period as the rotational period of the orbited body is called a synchronous orbit. If the inclination is also 0° and there is no eccentricity it is called a stationary orbit. A satellite in this orbit doesn't appear to move when viewed from the body's surface.
Kerbisynchronous equatorial orbit (KEO)
- → Main article: KEO
The stationary orbit around Kerbin, where the orbiting craft appears to stand still at a point above Kerbin's equator. The name was chosen to abbreviate it similar to GEO the abbreviation for geostationary orbit, which is the real world equivalent on the Earth.
Other
Various other orbits can be defined. The list of orbits on Wikipedia contain many common ones in the real world. They can be recreated by modifying the core features of the orbit to match the smaller universe. Some kind of orbits, like a sun-synchronous orbit around Earth, are not possible, because they require Kerbin's gravity to be not perfect. Also the Lagrange points do not exist so orbits near/around a Lagrange point are impossible. But it is possible to imitate L4 and L5, although every orbit with the same semi-major axis has the same orbital period, so L4 and L5 aren't special positions then.
Suborbital
An orbit is suborbital if the periapsis is below the surface and/or atmosphere(if the orbited body has one). A craft on a suborbital trajectory will most likely crash into the surface or land on it without finishing a complete orbit. Lifting surfaces like wings and parachutes might delay this.
Orbits in the save file
The save files (and scenarios) in KSP are plain text and human readable with the information on the orbit of every craft currently in the game. Most text editors allow to search for name = [Name of craft] via ^ Ctrl+F (⌘Cmnd+F for Mac). This locates the craft quickly in the file. The orbit section of the persistent.sfs should looks something like this:
ORBIT
{
SMA = 76875.4600066045
ECC = 0.136808532664149
INC = 32.6082297441138
LPE = 91.4665699628126
LAN = 305.802690796769
MNA = 0.556028537338098
EPH = 19189976.1161395
REF = 3
OBJ = 0
}
Each of these terms has a physical meaning and together they define an orbit. Changing them (and then re-loading the save game) will change the orbit of the vessel in question.
The first five parameters uniquely define a Keplerian trajectory:
- Eccentricity (ECC) and semimajor axis (SMA) specify, respectively, the shape of the trajectory (0 = circular, < 1 = elliptic, 1 = parabolic, > 1 = hyperbolic) and its size (half the distance between apsides, or equivalently, average of apsides as measured from the centre of the body). Hyperbolic orbits have a negative "semimajor axis" which relates to the mathematical definition of a hyperbola as a mirrored pair of curves, of which the orbit is one branch. However due to KSP's system of spheres of influence, an object can have an elliptic orbit (positive semimajor axis and eccentricity below 1) and still be escaping.
- Inclination (INC) and longitude of ascending node (LAN) specify the tilt of the orbital plane (anticlockwise from the ecliptic at the ascending node) and its orientation (anticlockwise from the vernal point to the ascending node). On Earth, the vernal point is the point on the celestial sphere where the sun is at the vernal equinox in the northern hemisphere (the ascending node of the ecliptic relative to the celestial equator). Since Kerbin has no axial tilt, the vernal point is arbitrary.
- Longitude of periapsis (LPE) specifies the orientation of the orbit within its plane (angle anticlockwise from the ascending node to the periapsis).
Then the object's position on the orbit at a given time is extrapolated from
- Epoch (EPH), a reference time, and
- Mean anomaly at epoch (MNA), a pseudo-angle (up to 2π) expressing the proportion of the orbital period that has passed since last periapsis. It's the angle of the corresponding position on a circular orbit. For hyperbolic orbits, this is negative if approaching periapsis, positive if receding from it.
These numbers are put into context by:
- REF : a reference number giving the celestial body that the object is orbiting. See below for a table.
- OBJ : Some sort of object reference (I wouldn't change this number). Possibly a code for the icon displayed - it appears that 0 corresponds to probes, and 1 corresponds to debris.
Angles are in radians, distances in meters.
By altering these values in the save file, one can easily "slew" vehicles into any position desired. This is very useful for setting up scenarios.
Reference code
This is a table contain the reference codes for all bodies of the Kerbol System:
| Planets/Stars | Moons | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Code | Name | Code | Name |
| 0 | Kerbol | ||
| 4 | Moho | ||
| 5 | Eve | 13 | Gilly |
| 1 | Kerbin | 2 | Mun |
| 3 | Minmus | ||
| 6 | Duna | 7 | Ike |
| 15 | Dres | ||
| 8 | Jool | 9 | Laythe |
| 10 | Vall | ||
| 12 | Tylo | ||
| 11 | Bop | ||
| 14 | Pol | ||
| 16 | Eeloo | ||
Notes
External links
- Orbit on Wikipedia
- Apsis on Wikipedia
- Low Earth orbit on Wikipedia
- Kraft, D and Townsend, G. (1963). NASA Orbital Flight Handbook, Part 1 - Basic Techniques and Data. Space Flight Handbooks, Vol. 1. http://ntrs.nasa.gov/search.jsp?R=19630011221
- For an enormous table of Keplerian element equations, see pdf page 126/document page III-16.