Difference between revisions of "Kerbin"
Kosmoshomar (talk | contribs) m (Changed the part about Kerbin being one of the 2 bodies with a breathable atmosphere.) |
m (fixed some grammar) |
||
| (67 intermediate revisions by 28 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | |||
{{Infobox/Body}} | {{Infobox/Body}} | ||
| + | '''Kerbin''' is the home planet of the [[Kerbal]]s, the location of the [[Kerbal Space Center|Space Center]] and other facilities, and the main focus of [[Kerbal Space Program]]. It is also the [[w:Earth|Earth]] analog for the game but, unlike Earth, it has two [[moon]]s instead of one. They are named '''[[the Mun]]''' and '''[[Minmus]]'''. It is the planet you start your game on, being home to the [[KSC]], where you construct and launch your vehicles on. | ||
| − | + | Kerbin, the home planet in Kerbal Space Program, boasts two natural satellites: the larger Mun and the smaller Minmus. The Mun, resembling Earth's moon, is characterized by its gray, cratered surface, offering ample opportunities for exploration and scientific research. In contrast, Minmus is a unique celestial body with a mint-green hue and low gravity, making it an ideal location for mining operations and testing advanced rover technologies. Both moons orbit Kerbin in slightly eccentric orbits, providing players with diverse challenges and objectives for their space missions. | |
| − | Kerbin is the third planet in [[orbit]] around the star [[Kerbol]]. It is the third largest [[celestial body]] that orbits Kerbol, following [[Jool]] and [[Eve]]. Jool's moon [[Tylo]] has the same radius of Kerbin, though it may be classified as larger, as the highest point on Tylo is about 5 km higher than the highest point on Kerbin. However, Tylo has only 80% of Kerbin's mass. | + | Kerbin is the third planet in [[orbit]] around the star [[Kerbol]]. It is the third largest [[celestial body]] that orbits Kerbol, following [[Jool]] and [[Eve]]. Jool's moon, [[Tylo]] has the same radius of Kerbin, though it may be classified as larger, as the highest point on [[Tylo]] is about 5 km higher than the highest point on Kerbin. However, [[Tylo]] has only 80% of Kerbin's mass. |
| − | Reaching a stable orbit around Kerbin is one of the first milestones a player might achieve in the game. With the introduction of version [[1.0.3]], attaining low Kerbin orbit requires a [[delta-v|Δv]] of approximately 3400 m/s | + | Reaching a stable orbit around Kerbin is one of the first milestones a player might achieve in the game. With the introduction of version [[1.0.3]], attaining low Kerbin orbit requires a [[delta-v|Δv]] of approximately 3400 m/s, though the exact amount depends on the efficiency of the ascent profile and the aerodynamics of the launch vehicle and payload. The only rocky planet that requires a higher Δv to attain orbit is [[Eve]] due to its dense atmosphere and higher gravity. Many interplanetary missions expend over half of their Δv in reaching Kerbin orbit. The velocity required to escape a body from a given altitude is always exactly the square root of two, times the velocity of a circular orbit around the body at that height: <math> (\sqrt{2}*v) </math>. |
== In-game description == | == In-game description == | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''KSP 1:''' | ||
{{Quote | {{Quote | ||
|A unique world, Kerbin has flat plains, soaring mountains and wide, blue oceans. Home to the Kerbals, it has just the right conditions to support a vast, seemingly undepletable population of the eager green creatures.<br /> | |A unique world, Kerbin has flat plains, soaring mountains and wide, blue oceans. Home to the Kerbals, it has just the right conditions to support a vast, seemingly undepletable population of the eager green creatures.<br /> | ||
| Line 12: | Line 16: | ||
''Reaching a stable orbit around Kerbin is one of the first things budding space programs strive for. It is said that those who can get their ship into orbit are halfway to anywhere.'' | ''Reaching a stable orbit around Kerbin is one of the first things budding space programs strive for. It is said that those who can get their ship into orbit are halfway to anywhere.'' | ||
|[[Kerbal Astronomical Society]]}} | |[[Kerbal Astronomical Society]]}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''KSP 2:''' | ||
| + | {{Quote | ||
| + | |Even as rockets and probes escape its atmosphere for deep space exploration, there is still much to appreciate about this vibrant world. Its vast oceans, deserts, forests, and plains coat the surface in lively beauty. Its moons, Mun and Minmus, swirl silently above it. Kerbalkind is fortunate to call this pale blue planet their home.|}} | ||
== Topography == | == Topography == | ||
| Line 18: | Line 26: | ||
[[File:Kerbinpeak.png|thumb|left|A Kerbal at Kerbin's highest peak(1.12.2)]] | [[File:Kerbinpeak.png|thumb|left|A Kerbal at Kerbin's highest peak(1.12.2)]] | ||
| − | Kerbin has a roughly equal distribution of [[ocean|liquid surface water]] and solid land, with polar ice caps and scattered deserts. Some of its mountains exceed 6 kilometers in height, with the tallest peak being 6767.4 m in altitude at the coordinates | + | Kerbin has a roughly equal distribution of [[ocean|liquid surface water]] and solid land, with polar ice caps and scattered deserts. Some of its mountains exceed 6 kilometers in height, with the tallest peak being 6767.4 m in altitude at the coordinates 46°21'32" E 61°35'53" N. The lowest point is almost 1.4 km deep and about 313° south-west of the Kerbal Space Center. |
=== Craters === | === Craters === | ||
| Line 165: | Line 173: | ||
A [[synchronous orbit]] is achieved with a semi-major axis of {{OrbitAltitude|b=Kerbin|f=k|3=0}}. [[KEO|Kerbisynchronous Equatorial Orbit (KEO)]] (or geostationary), has a circularly uniform altitude of {{OrbitAltitude|b=Kerbin|f=k}} and a speed of {{OrbitVelocity|b=Kerbin}}. From a 70 km low equatorial orbit, the periapsis maneuver requires 676.5 m/s and the apoapsis maneuver requires 434.9 m/s. A synchronous [[w:Tundra orbit|Tundra orbit]] with eccentricity of 0.2864 and inclination of 63 degrees is achieved at 3799.7/1937.7 km. Inclination correlates with eccentricity: higher inclined orbits need to be more eccentric, while equatorial orbit may be circular, essentially KEO. | A [[synchronous orbit]] is achieved with a semi-major axis of {{OrbitAltitude|b=Kerbin|f=k|3=0}}. [[KEO|Kerbisynchronous Equatorial Orbit (KEO)]] (or geostationary), has a circularly uniform altitude of {{OrbitAltitude|b=Kerbin|f=k}} and a speed of {{OrbitVelocity|b=Kerbin}}. From a 70 km low equatorial orbit, the periapsis maneuver requires 676.5 m/s and the apoapsis maneuver requires 434.9 m/s. A synchronous [[w:Tundra orbit|Tundra orbit]] with eccentricity of 0.2864 and inclination of 63 degrees is achieved at 3799.7/1937.7 km. Inclination correlates with eccentricity: higher inclined orbits need to be more eccentric, while equatorial orbit may be circular, essentially KEO. | ||
| − | A [[w:semi-synchronous orbit|semi-synchronous orbit]] with an orbital period of ½ of Kerbin's rotation period (2 h 59 m& | + | A [[w:semi-synchronous orbit|semi-synchronous orbit]] with an orbital period of ½ of Kerbin's rotation period (2 h 59 m 34.7 s or 10774.7 seconds) is achieved at an altitude of {{OrbitAltitude|b=Kerbin|f=k|pf=1/2}} with an orbital velocity of {{OrbitVelocity|b=Kerbin|pf=1/2}}. A semi-synchronous [[w:Molniya orbit|Molniya orbit]] with eccentricity of 0.742<ref>“[http://www.uwgb.edu/dutchs/AstronNotes/Orbits0.HTM Some Major Orbit Types]” uses that, [[w:Molniya orbit#References|the Wikipedia article]] mentions 0.74105, and “[http://www.eumetcal.org/euromet/english/satmet/s3220/s3220332.htm Orbital Parameters of a Molniya Orbit]” uses 0.72.</ref> and inclination of 63 degrees can not be achieved, because the periapsis would be 36 km below the ground. The highest eccentricity of a semi-synchronous orbit with a periapsis of 70 km is 0.693<!---389102957193457747187874683092468355009655955115825698569= (1585.18 + 600-670)/(1585.18 + 600)--> with an apoapsis of 3100.36<!-- (1585.18+600)*2-670-600 --> km. |
The [[w:Hill sphere|Hill sphere]] (the radius around the planet at which moons are gravitationally stable) of Kerbin is 136 185 km, or roughly 227 Kerbin radii. | The [[w:Hill sphere|Hill sphere]] (the radius around the planet at which moons are gravitationally stable) of Kerbin is 136 185 km, or roughly 227 Kerbin radii. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Low Kerbin Orbit === | ||
| + | |||
| + | Space near Kerbin is 70 to 249km, as found in science experiments, so LKO is 70 to 249km. | ||
| + | |||
| + | === High Kerbin Orbit === | ||
| + | |||
| + | Space high above Kerbin is 250 to ~84000km (end of SOI), as found in science experiments, so HKO is 250 to ~84000km. | ||
== Delta-V Requirements == | == Delta-V Requirements == | ||
| − | From the lowest possible stable orbit around Kerbin (70 km), the | + | From the lowest possible stable orbit around Kerbin (70 km), the average amount of delta-V needed to reach other destinations is: |
{| class="wikitable" | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| Line 199: | Line 215: | ||
== Reference frames == | == Reference frames == | ||
{{:Kerbin/RefFrame}} | {{:Kerbin/RefFrame}} | ||
| + | |||
| + | == KSP 2 == | ||
| + | === Surface Research Locations === | ||
| + | Surface research locations include: | ||
| + | * Grasslands | ||
| + | * Highlands | ||
| + | * Mountains | ||
| + | * Desert | ||
| + | * Ice | ||
| + | * Water | ||
| + | * Beach | ||
| + | |||
| + | === Maps === | ||
| + | ==== Biomes ==== | ||
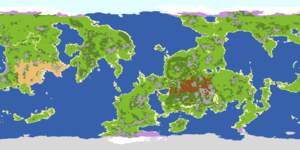
| + | [[File:kerbin_region_ui.jpg|thumb|none|Kerbin biome map with legend (as of v0.2.1.0 (from Orbital Survey mod))]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Visual map ==== | ||
| + | [[File:kerbin_visual.png|thumb|none|Eve visual map (as of v0.2.1.0)]] | ||
| + | [https://i.imgur.com/qpbtPbl.png Kerbin visual map (Imgur)] | ||
| + | |||
== Gallery == | == Gallery == | ||
| + | === [[Kerbal Space Program]] === | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
Kerbin ISA Topo 0 21.jpg |Topographical map of Kerbin as of {{version|0.21}} | Kerbin ISA Topo 0 21.jpg |Topographical map of Kerbin as of {{version|0.21}} | ||
| Line 215: | Line 252: | ||
Screenshot255.png | Kerbin's South Pole | Screenshot255.png | Kerbin's South Pole | ||
Solar eclipse in LKO.jpg | A solar eclipse from low Kerbin orbit (LKO). | Solar eclipse in LKO.jpg | A solar eclipse from low Kerbin orbit (LKO). | ||
| − | + | Entire kerbin system.jpg | Kerbin and Minmus seen from the surface of the Mun. | |
| − | + | KSPKerbalSystem.PNG | Kerbin, Mun, and Minmus in a line, seen from a Minmus landing craft. | |
| + | KerbinSystemPhoto.png | Another picture of the kerbin system, seen from near-Minmus space | ||
| + | </gallery> | ||
| + | === [[Kerbal Space Program 2]] === | ||
| + | <gallery> | ||
| + | KSP2 Kerbin Horizon.png|The horizon of Kerbin in KSP2. | ||
| + | KSP2 Grass.png|Grass on Kerbin in KSP2. | ||
| + | KSP2 Flowers.png|Flowers on Kerbin in KSP2. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
| Line 237: | Line 281: | ||
* Added biomes. | * Added biomes. | ||
;[[1.0.5]] | ;[[1.0.5]] | ||
| − | * Kerbin | + | * Kerbin spun up to have a 6 hour synodic day. |
;[[0.90]] | ;[[0.90]] | ||
* Updated biomes. | * Updated biomes. | ||
| Line 275: | Line 319: | ||
[[File:KerbinBiomeMap.png|left|thumb|The biomes on Kerbin as of 0.90]] | [[File:KerbinBiomeMap.png|left|thumb|The biomes on Kerbin as of 0.90]] | ||
| − | * The quote from the [[Kerbal Astronomical Society]] is true. | + | * The quote from the [[Kerbal Astronomical Society]] is true. in real life (and in Kerbal Space Program), during a one-way interplanetary mission, half the delta v is expended on orbit. |
=== Real-world comparison === | === Real-world comparison === | ||
| − | Kerbin has approximately | + | Kerbin has approximately one-tenth the radius of Earth and 1/113th the mass. |
== See also == | == See also == | ||
Latest revision as of 23:46, 16 October 2024
| Kerbin | ||
| Kerbin as seen from orbit. | ||
| Planet of Kerbol | ||
| Orbital Characteristics | ||
| Semi-major axis | 13 599 840 256 m [Note 1] | |
| Apoapsis | 13 599 840 256 m [Note 1] | |
| Periapsis | 13 599 840 256 m [Note 1] | |
| Orbital eccentricity | 0 | |
| Orbital inclination | 0 ° | |
| Argument of periapsis | 0 ° | |
| Longitude of the ascending node | 0 ° | |
| Mean anomaly | 3.14 rad (at 0s UT) | |
| Sidereal orbital period | 9 203 545 s | |
| 426 d 0 h 32 m 24.6 s | ||
| Synodic orbital period | Not defined | |
| Orbital velocity | 9 285 m/s | |
| Physical Characteristics | ||
| Equatorial radius | 600 000 m | |
| Equatorial circumference | 3 769 911 m | |
| Surface area | 4.5238934×1012 m2 | |
| Mass | 5.2915158×1022 kg | |
| Standard gravitational parameter | 3.5316000×1012 m3/s2 | |
| Density | 58 484.090 kg/m3 | |
| Surface gravity | 9.81 m/s2 (1 g) | |
| Escape velocity | 3 431.03 m/s | |
| Sidereal rotation period | 21 549.425 s | |
| 5 h 59 m 9.4 s | ||
| Solar day | 21 600.000 s | |
| 5 h 59 m 60 s | ||
| Sidereal rotational velocity | 174.94 m/s | |
| Synchronous orbit | 2 863.33 km | |
| Sphere of influence | 84 159 286 m [Note 1] | |
| Atmospheric Characteristics | ||
| Atmosphere present | Yes | |
| Atmospheric pressure | 101.325 kPa | |
| 1 atm | ||
| Atmospheric height | 70 000 m | |
| 1.0×10-6 atm | ||
| Temperaturemin | -86.20 °C 186.95 K | |
| Temperaturemax | 15 °C 288.15 K | |
| Oxygen present | Yes | |
| Scientific multiplier | ||
| Surface | 0.3 | |
| Splashed | 0.4 | |
| Lower atmosphere | 0.7 | |
| Upper atmosphere | 0.9 | |
| Near space | 1 | |
| Outer space | 1.5 | |
| Recovery | 1 | |
|
| ||
Kerbin is the home planet of the Kerbals, the location of the Space Center and other facilities, and the main focus of Kerbal Space Program. It is also the Earth analog for the game but, unlike Earth, it has two moons instead of one. They are named the Mun and Minmus. It is the planet you start your game on, being home to the KSC, where you construct and launch your vehicles on.
Kerbin, the home planet in Kerbal Space Program, boasts two natural satellites: the larger Mun and the smaller Minmus. The Mun, resembling Earth's moon, is characterized by its gray, cratered surface, offering ample opportunities for exploration and scientific research. In contrast, Minmus is a unique celestial body with a mint-green hue and low gravity, making it an ideal location for mining operations and testing advanced rover technologies. Both moons orbit Kerbin in slightly eccentric orbits, providing players with diverse challenges and objectives for their space missions.
Kerbin is the third planet in orbit around the star Kerbol. It is the third largest celestial body that orbits Kerbol, following Jool and Eve. Jool's moon, Tylo has the same radius of Kerbin, though it may be classified as larger, as the highest point on Tylo is about 5 km higher than the highest point on Kerbin. However, Tylo has only 80% of Kerbin's mass.
Reaching a stable orbit around Kerbin is one of the first milestones a player might achieve in the game. With the introduction of version 1.0.3, attaining low Kerbin orbit requires a Δv of approximately 3400 m/s, though the exact amount depends on the efficiency of the ascent profile and the aerodynamics of the launch vehicle and payload. The only rocky planet that requires a higher Δv to attain orbit is Eve due to its dense atmosphere and higher gravity. Many interplanetary missions expend over half of their Δv in reaching Kerbin orbit. The velocity required to escape a body from a given altitude is always exactly the square root of two, times the velocity of a circular orbit around the body at that height: .
Contents
In-game description
KSP 1:
| “ | A unique world, Kerbin has flat plains, soaring mountains and wide, blue oceans. Home to the Kerbals, it has just the right conditions to support a vast, seemingly undepletable population of the eager green creatures.
|
” |
KSP 2:
| “ | Even as rockets and probes escape its atmosphere for deep space exploration, there is still much to appreciate about this vibrant world. Its vast oceans, deserts, forests, and plains coat the surface in lively beauty. Its moons, Mun and Minmus, swirl silently above it. Kerbalkind is fortunate to call this pale blue planet their home. | ” |
Topography
Kerbin has a roughly equal distribution of liquid surface water and solid land, with polar ice caps and scattered deserts. Some of its mountains exceed 6 kilometers in height, with the tallest peak being 6767.4 m in altitude at the coordinates 46°21'32" E 61°35'53" N. The lowest point is almost 1.4 km deep and about 313° south-west of the Kerbal Space Center.
Craters
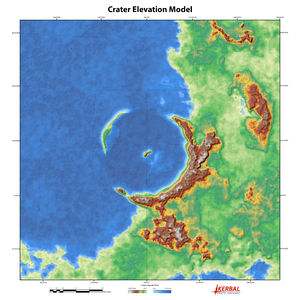
Unlike other bodies in its system, Kerbin has few visible craters because its environment would erode craters from the few meteors that avoid the gravity or surface of its large moon and survive entry. Nevertheless, some geological formations indicate that bodies have violently collided with Kerbin: a planetary feature appears to be an impact crater, while a secondary rupture lies on the other side of the planet (made by the intense longitudinal, or P-wave earthquakes that ensue.) Both are in excess of 100 km diameter, and the main crater lies along the far-western coastline. The uplift is easily visible as a series of islands, and the feature has a central peak that pokes up through the water (also known as a rebound peak.) The other, and smaller of the two, is near the prime meridian in the northern hemisphere and is more easily missed, but its uplift rims are visible, and it also has a central rebound peak.
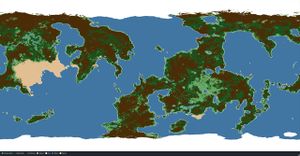
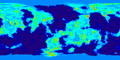
Biomes
After the Mun, Kerbin is the celestial body with the second-highest number of biomes. Science experiments can be performed in all biomes, though Kerbin's low multipliers result in less impressive results than more distant worlds. Kerbin's biomes show a loose correlation with Earth's biomes and geographic features. Uniquely, Kerbin has 33 location biomes at KSC, these are comprised of each building and their props, the crawlerway, the flag, and KSC itself; these give a jumpstart to gathering Science points in Career mode. With 1.2 Kerbin had distinct Northern and Southern Ice Shelves added.
|
List of biomes
KSC mini biomes
|
Atmosphere
Kerbin has a thick, warm atmosphere with a mass of approximately 4.7×1016 kilograms, a sea level pressure of 101.325 kilopascals (1 atmosphere), and a depth of 70,000 meters. The atmosphere contains oxygen and can support combustion. Kerbin is one of the two celestial bodies (the other one being Laythe) with a breathable atmosphere.
The average molecular weight of Kerbin air is 28.9644 g/mol, and its adiabatic index is 1.40. This suggests that Kerbin likely has an earthlike nitrogen-oxygen atmosphere. The air-fuel ratio of jet engines operating in Kerbin's atmosphere suggests that the percentage of oxygen is similar to that of Earth's atmosphere (about 21%).
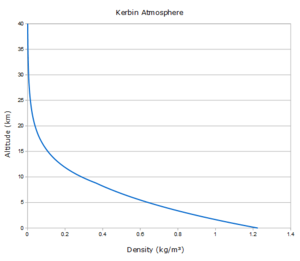
Like all other atmospheres in the game, Kerbin's atmosphere fades exponentially as altitude increases. The scale height varies with altitude, which is a change from pre-1.0 versions of the game. The pressure-altitude profile is globally constant and independent of temperature. The following table gives the atmospheric pressure and density at various altitudes above sea level. Temperature-altitude profile is not globally constant, therefore neither is the density-altitude profile, however variance is slight.
| Altitude (m) | Pressure (Pa) | Pressure (atm) | Density (kg/m^3) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 101 325 | 1.000 | 1.225 |
| 2 500 | 69 015 | 0.681 | 0.898 |
| 5 000 | 45 625 | 0.450 | 0.642 |
| 7 500 | 29 126 | 0.287 | 0.446 |
| 10 000 | 17 934 | 0.177 | 0.288 |
| 15 000 | 6 726 | 0.066 | 0.108 |
| 20 000 | 2 549 | 0.025 | 0.040 |
| 25 000 | 993.6 | 0.010 | 0.015 |
| 30 000 | 404.1 | 0.004 | 0.006 |
| 40 000 | 79.77 | 0.001 | 0.001 |
| 50 000 | 15.56 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 60 000 | 2.387 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
| 70 000 | 0.000 | 0.000 | 0.000 |
Kerbin's atmosphere can be divided into three major layers, comparable to Earth's troposphere, stratosphere and mesosphere. In the lower and upper layers, temperature decreases as altitude increases, while the middle layer spans of a region of increasing temperature. The boundary between the lower and middle layers occurs at an altitude of about 16 km at low latitudes, and about 9 km at high latitudes. The boundary between the middle and upper layer occurs at an altitude of about 38 km.
Air temperatures vary with latitude and time of day. At the equator, sea level temperatures vary between a nighttime low of 32 °C and a daytime high of 41 °C. At the poles, the temperature varies between -35 °C and -30 °C. The globally averaged sea level temperature is approximately 13.5 °C. Since Kerbin has no axial tilt, there are no seasonal temperature variations.
The atmosphere of Kerbin is patterned after Earth's U.S. Standard Atmosphere (USSA), though with the vertical height scale reduced by 20%. Kerbin's "base" temperature and atmospheric pressure can be very closely approximated using the equations of the USSA, where Kerbin's geometric altitude, z, is converted to Earth's geopotential altitude, h, using the equation:
- .
The base temperature is the temperature less latitudinal and diurnal adjustments; it is roughly equal to the global mean temperature.
Atmospheric flight
The thickness of Kerbin's atmosphere makes it well suited for aerobraking from a high-speed interplanetary intercept. The periapsis altitude required for a successful aerocapture depends on the spacecraft's drag characteristics, its approach velocity, and the desired apoapsis of the resulting orbit. For most conditions, a periapsis altitude of about 30 km should result in an aerocapture.
Parachutes perform well in Kerbin's dense air, allowing landings on both land and water to be accomplished without the aid of propulsion.
Because of the presence of oxygen, jet engines can operate in Kerbin's atmosphere. And, together with its thickness, Kerbin's atmosphere is ideally suited for aircraft flight.
Orbits
A synchronous orbit is achieved with a semi-major axis of 3 463.33 km. Kerbisynchronous Equatorial Orbit (KEO) (or geostationary), has a circularly uniform altitude of 2 863.33 km and a speed of 1 009.81 m/s. From a 70 km low equatorial orbit, the periapsis maneuver requires 676.5 m/s and the apoapsis maneuver requires 434.9 m/s. A synchronous Tundra orbit with eccentricity of 0.2864 and inclination of 63 degrees is achieved at 3799.7/1937.7 km. Inclination correlates with eccentricity: higher inclined orbits need to be more eccentric, while equatorial orbit may be circular, essentially KEO.
A semi-synchronous orbit with an orbital period of ½ of Kerbin's rotation period (2 h 59 m 34.7 s or 10774.7 seconds) is achieved at an altitude of 1 581.76 km with an orbital velocity of 1 272.28 m/s. A semi-synchronous Molniya orbit with eccentricity of 0.742[1] and inclination of 63 degrees can not be achieved, because the periapsis would be 36 km below the ground. The highest eccentricity of a semi-synchronous orbit with a periapsis of 70 km is 0.693 with an apoapsis of 3100.36 km.
The Hill sphere (the radius around the planet at which moons are gravitationally stable) of Kerbin is 136 185 km, or roughly 227 Kerbin radii.
Low Kerbin Orbit
Space near Kerbin is 70 to 249km, as found in science experiments, so LKO is 70 to 249km.
High Kerbin Orbit
Space high above Kerbin is 250 to ~84000km (end of SOI), as found in science experiments, so HKO is 250 to ~84000km.
Delta-V Requirements
From the lowest possible stable orbit around Kerbin (70 km), the average amount of delta-V needed to reach other destinations is:
| Body | Δv |
|---|---|
| Mun | ~860 m/s |
| Minmus | ~930 m/s |
| Eve | ~1033 m/s |
| Duna | ~1060 m/s |
| Geostationary Orbit | ~1120 m/s |
| Dres | ~1540 m/s |
| Moho | ~1676 m/s |
| Jool | ~1915 m/s |
| Eeloo | ~2100 m/s |
| Kerbol escape | ~2740 m/s |
Reference frames
| Time warp | Minimum Altitude |
|---|---|
| 1× | Any |
| 5× | 70 000 m (above the atmosphere) |
| 10× | 70 000 m (above the atmosphere) |
| 50× | 70 000 m (above the atmosphere) |
| 100× | 120 000 m |
| 1 000× | 240 000 m |
| 10 000× | 480 000 m |
| 100 000× | 600 000 m |
KSP 2
Surface Research Locations
Surface research locations include:
- Grasslands
- Highlands
- Mountains
- Desert
- Ice
- Water
- Beach
Maps
Biomes
Visual map
Gallery
Kerbal Space Program
Topographical map of Kerbin as of version 0.21
A projection map of Kerbin, as of 0.14.1 and before (including the old demo).
Topographical image of Kerbin from 0.17.1. The terrain is slightly different in the latest version.[2]
Kerbal Space Program 2
Changes
- KSC's grass now changes according to the currently set terrain shader quality.
- Added biomes.
- Kerbin spun up to have a 6 hour synodic day.
- Updated biomes.
- Biomes added.
- Terrain revised to produce more detailed and interesting landforms.
- Fixed ladders on the fuel tanks near the launchpad.
- New mesh for the launchpad and area (no launchtower anymore).
- New mesh for the runway, with lights and sloping edges for rovers.
- Terrain overhaul: Entire planet redo. Deserts, darker and greener grass, islands, darker ocean/water, snow capped mountains. Looks more realistic.
- Several Easter Eggs added.
- Airport added to island off of KSC coastline. (Not a launching point)
- Improved atmosphere visuals.
- Minmus was added.
- Much more varied and taller terrain was added. Prior to this, some mountain ranges exceeded 600 m in height, but the tallest point was at an altitude of approximately 900 meters.
- Mun added.
- Terrain overhaul, oceans became wet.
- Atmosphere extended from ~34,500 m to ~69,000 m.
- Initial Release
Trivia
- Kerbin's continents are derived from libnoise[3], a coherent noise generating library, though they have been increasingly modified with time.
- Before 0.90 Kerbin was one of the few bodies with multiple Biomes. Following the 0.90 update all celestial bodies have biomes.
- The quote from the Kerbal Astronomical Society is true. in real life (and in Kerbal Space Program), during a one-way interplanetary mission, half the delta v is expended on orbit.
Real-world comparison
Kerbin has approximately one-tenth the radius of Earth and 1/113th the mass.
See also
- List of bases on Kerbin
- Kerbal Space Center
- Inland Kerbal Space Center
- Island Airfield
- Woomerang Launch Site
- Dessert Launch Site
- Dessert Airfield
Notes
- ↑ “Some Major Orbit Types” uses that, the Wikipedia article mentions 0.74105, and “Orbital Parameters of a Molniya Orbit” uses 0.72.
- ↑ http://forum.kerbalspaceprogram.com/entry.php/247-A-Brave-New-World
- ↑ http://libnoise.sourceforge.net/examples/complexplanet/